本文共 6283 字,大约阅读时间需要 20 分钟。
目录
一、Redis为什么需要持久化
因为Redis是内存数据库,它将自己的数据存储在内存里面,一旦Redis服务器进程退出或者运行Redis服务器的计算机停机,Redis服务器中的数据就会丢失。
为了避免数据丢失,所以Redis提供了持久化机制,将存储在内存中的数据保存到磁盘中,用于在Redis服务器进程退出或者运行Redis服务器的计算机停机导致数据丢失时,快速的恢复之前Redis存储在内存中的数据。
Redis提供了2种持久化方式,分别为:
- RDB持久化
- AOF持久化
二、RDB持久化
RDB持久化是将某个时间点上Redis中的数据保存到一个RDB文件中,如下所示:

RDB的持久化也叫快照持久化。快照持久化指的是将某一时刻的所有数据写入硬盘,快照是内存数据的二进制序列化形式,在存储上非常紧凑,而AOF日志记录的是内存数据修改的指令记录文本(即对应的SQL语句)。
RDB文件是一个经过压缩的二进制文件,通过该文件可以还原生成RDB文件时Redis中的数据,如下所示:

2.1 创建RDB文件
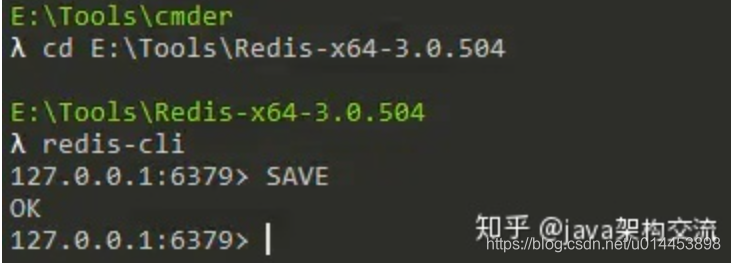
Redis提供了2个命令来创建RDB文件,一个是SAVE,另一个是BGSAVE。
SAVE命令会阻塞Redis服务器进程,直到RDB文件创建完毕为止,在服务器进程阻塞期间,服务器不能处理任何命令请求,如下所示:
BGSAVE命令会派生出一个子进程,然后由子进程负责创建RDB文件,服务器进程(父进程)继续处理命令请求,如下所示:
![]()
因为BGSAVE命令可以在不阻塞服务器进程的情况下执行,所以推荐使用BGSAVE命令。
我们可以手动执行该命令,如上面截图所示,但还是推荐设置下Redis服务器配置文件的save选项,让服务器每隔一段时间自动执行一次BGSAVE命令。
我们可以通过save选项设置多个保存条件,只要其中任意一个条件被满足,服务器就会执行BGSAVE命令。
save选项设置的默认条件如下所示:


默认的配置条件表示,只要满足以下3个条件中的任意1个,BGSAVE命令就会被执行:
- 服务器在900s(即15分钟)之内,对数据库进行了至少1次修改
- 服务器在300s(即5分钟)之内,对数据库进行了至少10次修改
- 服务器在60s(即1分钟)之内,对数据库进行了至少10000次修改
当满足条件执行BGSAVE命令时,输出日志如下图所示:

生成的RDB文件会根据Redis配置文件中的名称和路径来保存,相关的2个配置如下所示:

最终生成的RDB文件如下所示(截图为本机Windows环境,Linux环境下路径会稍有不同):
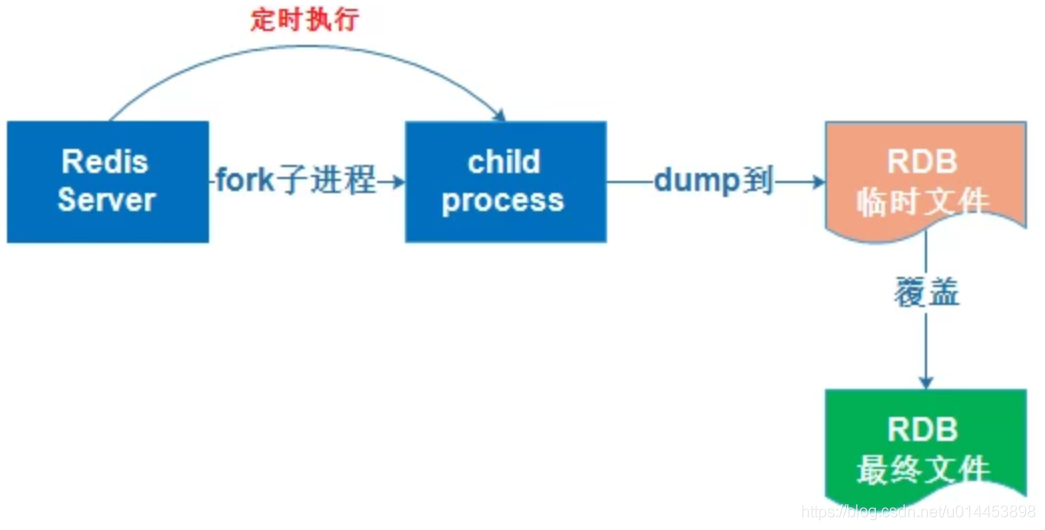
RDB持久化实际操作过程是fork一个子进程,先将数据集写入临时文件,写入成功后,再替换之前的文件,用二进制压缩存储。
2.2 载入RDB文件
首先,我们要明确的是,载入RDB文件的目的是为了在Redis服务器进程重新启动之后还原之前存储在Redis中的数据。
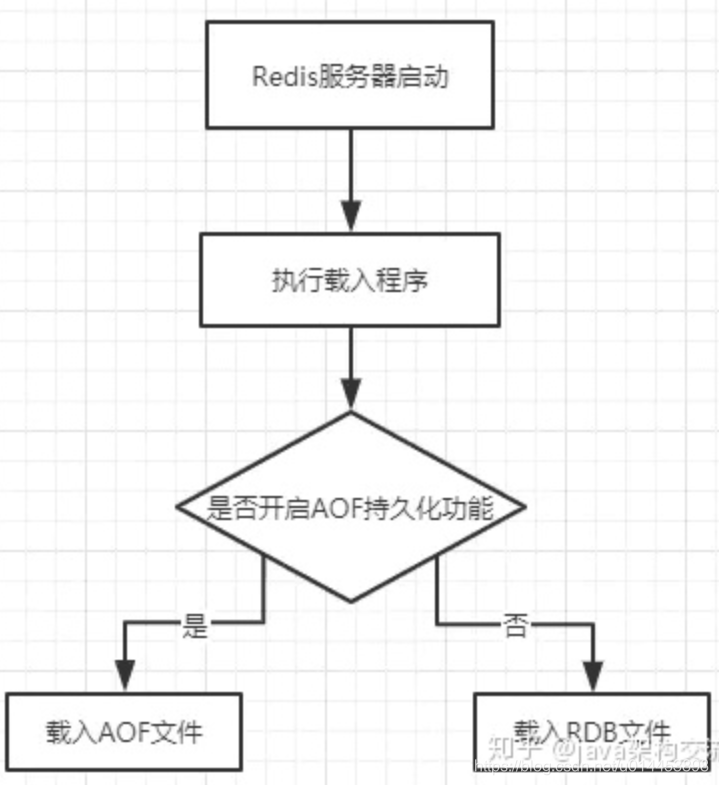
然后,Redis载入RDB文件并没有专门的命令,而是在Redis服务器启动时自动执行的。
而且,Redis服务器启动时是否会载入RDB文件还取决于服务器是否启用了AOF持久化功能,具体判断逻辑为:
- 只有在AOF持久化功能处于关闭状态时,服务器才会使用RDB文件来还原数据。
- 如果服务器开启了AOF持久化功能,那么服务器会优先使用AOF文件来还原数据。
默认情况下,Redis服务器的AOF持久化功能是关闭的,所以Redis服务器在启动时会载入RDB文件,启动日志如下所示:
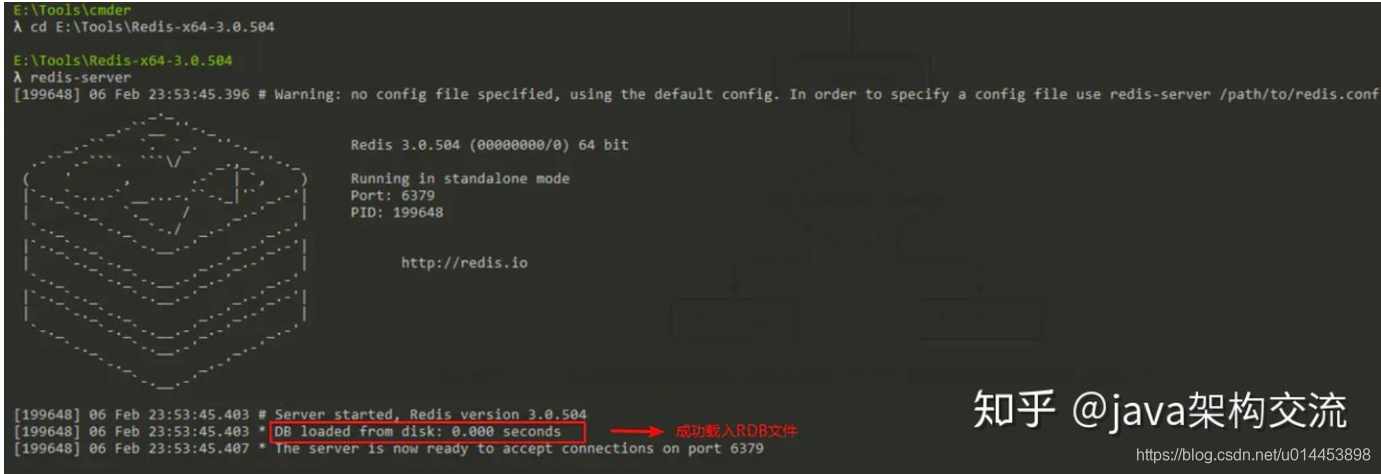
2.3 服务器状态
创建和载入RDB文件,可能存在的服务器状态有以下3种:
- 当执行SAVE命令时,Redis服务器会被阻塞,此时客户端发送的所有命令请求都会被阻塞,只有在服务器执行完SAVE命令,重新开始接受命令请求之后,客户端发送的命令请求才会被处理。
- 当执行BGSAVE命令时,Redis服务器不会被阻塞,Redis服务器仍然可以继续处理客户端发送的命令请求。
- 服务器在载入RDB文件期间,会一直处于阻塞状态,直到RDB文件载入成功。
三、AOF持久化
AOF持久化是通过保存Redis服务器所执行的写命令来记录(如SQL语句)数据库数据的,如下图所示:

默认情况下,AOF持久化功能是关闭的,如果想要打开,可以修改下图所示的配置:

举个例子,假设Redis中还没有存储任何数据,我们执行了如下所示的命令:
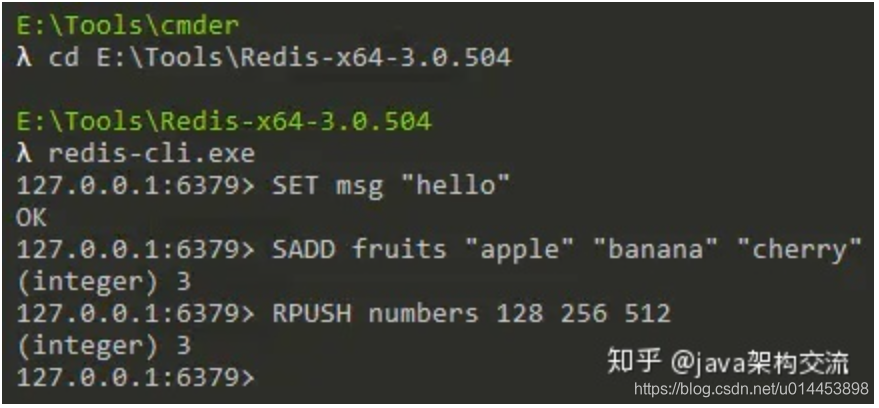
然后我们会发现Redis服务器生成了1个名为appendonly.aof的文件
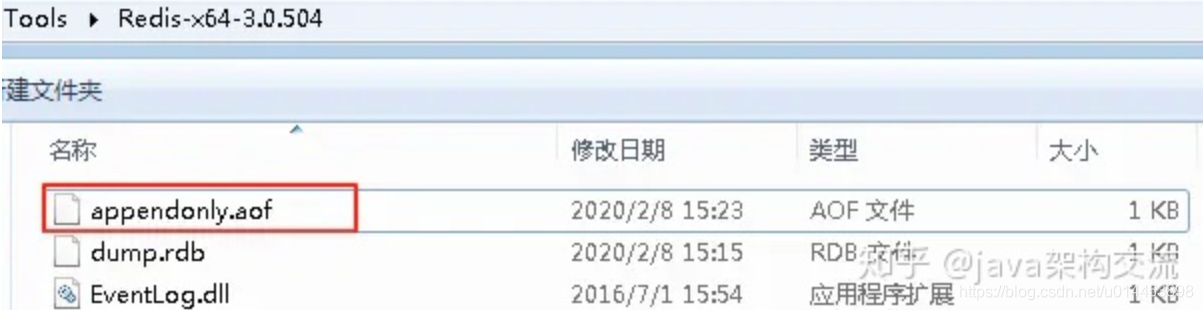
打开该文件,我们可以看到上面执行的3个写命令都存储在该文件中:

3.1 AOF持久化的实现
当AOF持久化功能处于打开状态时,Redis服务器在执行完一个写命令之后,会以协议格式(如上面截图中AOF文件里保存写命令的格式)将被执行的写命令追加到服务器状态的AOF缓冲区的末尾,然后Redis服务器会根据配置文件中appendfsync选项的值来决定何时将AOF缓冲区中的内容写入和同步到AOF文件里面。
appendfsync选项有以下3个值:
- always 从安全性来说,always是最安全的(丢失数据最少),因为即使出现故障停机,数据库也只会丢失一个事件循环中所产生的命令数据。 从效率来说,always的效率最慢,因为服务器在每个事件循环都要将AOF缓冲区中的所有内容写入到AOF文件,并且同步AOF文件。
- everysec 从安全性来说,everysec模式下,即使出现故障停机,数据库只会丢失一秒钟的命令数据。 从效率来说,everysec模式足够快,因为服务器在每个事件循环都要将AOF缓冲区中的所有内容写入到AOF文件,并且每隔一秒就要在子线程中对AOF文件进行同步。
- no 从安全性来说,no模式下,如果出现故障停机,数据库会丢失上次同步AOF文件之后的所有写命令数据,具有不确定性,因为服务器在每个事件循环都要将AOF缓冲区中的所有内容写入到AOF文件,至于何时对AOF文件进行同步,则由操作系统控制。 从效率来说,no模式和everysec模式的效率差不多。
appendfsync选项的默认值是everysec,也推荐使用这个值,因为既保证了效率又保证了安全性。
3.2 载入AOF文件
因为AOF文件包含了重建数据库所需的所有写命令,所以Redis服务器只要读入并重新执行一遍AOF文件里面保存的写命令,就可以还原Redis服务器关闭之前的数据。
如果Redis服务器开启了AOF持久化功能,那么Redis服务器在启动时会载入AOF文件,
启动日志如下所示:
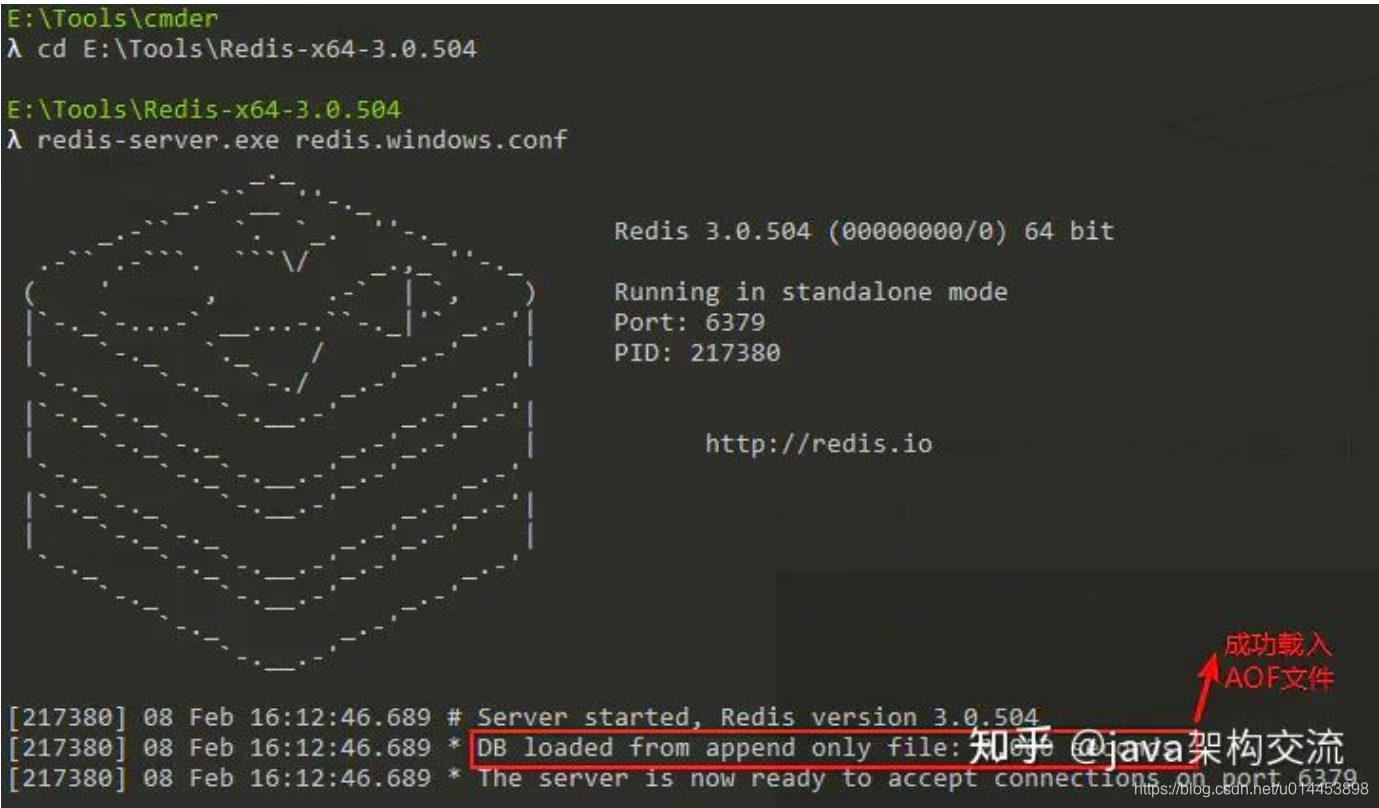
3.3 AOF重写
因为AOF持久化是通过保存被执行的写命令来记录数据库数据的,所以随着Redis服务器运行时间的增加,AOF文件中的内容会越来越多,文件的体积会越来越大,如果不做控制,会有以下2点坏处:
- 过多的占用服务器磁盘空间,可能会对Redis服务器甚至整个宿主计算机造成影响。
- AOF文件的体积越大,使用AOF文件来进行数据库还原所需的时间就越多。
举个例子,在客户端执行如下命令:

为了记录这个list键的状态,AOF文件就需要保存上面执行的6条命令。
为了解决AOF文件体积越来越大的问题,Redis提供了AOF文件重写功能,即Redis服务器会创建一个新的AOF文件来替代现有的AOF文件,新旧两个AOF文件所保存的数据库数据相同,但新AOF文件不会包含任何浪费空间的冗余命令,所以新AOF文件的体积通常会比旧AOF文件的体积要小很多。
3.3.1 AOF重写的原理
AOF文件重写并不需要对现有的AOF文件进行任何读取、分析或者写入操作,而是通过读取服务器当前的数据库数据来实现的。
仍然以上面的list键为例,旧的AOF文件保存了6条命令来记录list键的状态,但list键的结果是“C” "D" "E" "F" "G"这样的数据,所以AOF文件重写时,可以用一条RPUSH list “C” "D" "E" "F" "G"命令来代替之前的六条命令,这样就可以将保存list键所需的命令从六条减少为一条了。
按照上面的原理,如果Redis服务器存储的键值对足够多,AOF文件重写生成的新AOF文件就会减少很多很多的冗余命令,进而大大减小了AOF文件的体积。
综上所述,AOF文件重写功能的实现原理为:
首先从数据库中读取键现在的值,然后用一条命令去记录键值对,代替之前记录这个键值对的多条命令。
3.3.2 AOF后台重写
因为AOF文件重写会进行大量的文件写入操作,所以执行这个操作的线程将被长时间阻塞。
因为Redis服务器使用单个线程来处理命令请求,所以如果由服务器进程直接执行这个操作,那么在重写AOF文件期间,服务器将无法处理客户端发送过来的命令请求。
为了避免上述问题,Redis将AOF文件重写功能放到子进程里执行,这样做有以下2个好处:
- 子进程进行AOF文件重写期间,服务器进程(父进程)可以继续处理命令请求。
- 子进程带有服务器进程的数据副本,使用子进程而不是线程,可以在避免使用锁的情况下,保证数据的安全性。
AOF后台重写的步骤如下所示:
- 服务器进程创建子进程,子进程开始AOF文件重写
- 从创建子进程开始,服务器进程执行的所有写命令不仅要写入AOF缓冲区(用于数据持久化),还要写入AOF重写缓冲区 写入AOF缓冲区的目的是为了同步到原有的AOF文件(持久化)。 写入AOF重写缓冲区的目的是因为子进程在进行AOF文件重写期间,服务器进程还在继续处理命令请求, 而新的命令可能会对现有的数据库进行修改,从而使得服务器当前的数据库数据和重写后的AOF文件所 保存的数据库数据不一致。
- 子进程完成AOF重写工作,向父进程发送一个信号,父进程在接收到该信号后,会执行以下操作: 1.将AOF重写缓冲区中的所有内容写入到新AOF文件中,这样就保证了新AOF文件所保存的数据库数据和服务器当前的数据库数据是一致的。 2.对新的AOF文件进行改名,原子地覆盖现有的AOF文件,完成新旧两个AOF文件的替换。
3.3.3 AOF重写的触发方
AOF的重写可以由用户手动调用 BGREWRITEAOF 命令手动触发。如下图:

除了手动执行外,Redis还提供了2个配置项用来自动触发 BGREWRITEAOF 命令:
auto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100
auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mb
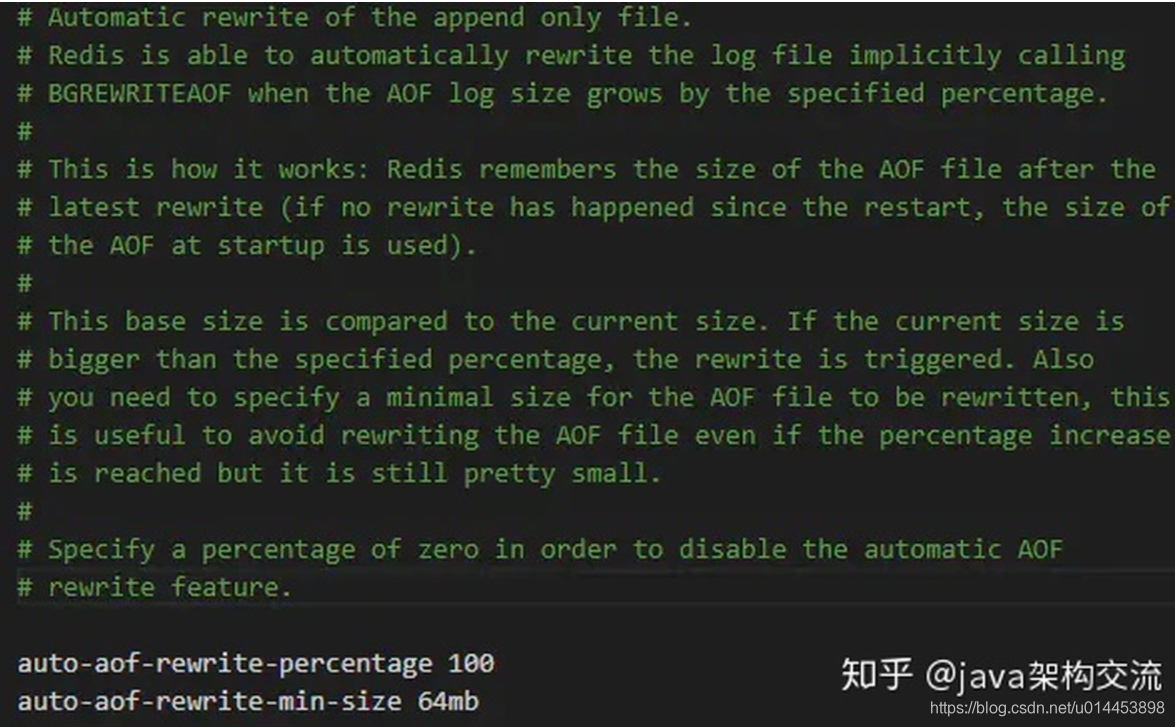
该配置表示,当AOF文件的d体积大于64MB,并且AOF文件的体积比上一次重写之后的体积大了至少一倍(100%),redis将自动执行 BGREWIRTEAOF 命令。
四、AOF和RDB持久化的区别
通过上面的讲解,我们会发现Redis提供的2种持久化方法是有区别的,可以总结为以下4点:
- 实现方式
- 文件体积
- 安全性
- 优先级
4.1 实现方式
RDB持久化是通过将某个时间点Redis服务器存储的数据保存到RDB文件中来实现持久化的。(快照)
AOF持久化是通过将Redis服务器执行的所有写命令保存到AOF文件中来实现持久化的。(SQL写命令)
4.2 文件体积
由上述实现方式可知,RDB持久化记录的是结果,AOF持久化记录的是过程,所以AOF持久化生成的AOF文件会有体积越来越大的问题,Redis提供了AOF重写功能来减小AOF文件体积。
4.3 安全性
AOF持久化的安全性要比RDB持久化的安全性高,即如果发生机器故障,AOF持久化要比RDB持久化丢失的数据要少。
因为RDB持久化会丢失上次RDB持久化后写入的数据,而AOF持久化最多丢失1s之内写入的数据(使用默认everysec配置的话)。
4.4 优先级
由于上述的安全性问题,如果Redis服务器开启了AOF持久化功能,Redis服务器在启动时会使用AOF文件来还原数据,如果Redis服务器没有开启AOF持久化功能,Redis服务器在启动时会使用RDB文件来还原数据,所以AOF文件的优先级比RDB文件的优先级高。(但redis默认的是RDB)
4.5 优缺点
RDB存在哪些优势呢?
1). 一旦采用该方式,那么你的整个Redis数据库将只包含一个文件,这对于文件备份而言是非常完美的。比如,你可能打算每个小时归档一次最近24小时的数据,同时还要每天归档一次最近30天的数据。通过这样的备份策略,一旦系统出现灾难性故障,我们可以非常容易的进行恢复。
2). 对于灾难恢复而言,RDB是非常不错的选择。因为我们可以非常轻松的将一个单独的文件压缩后再转移到其它存储介质上。
3). 性能最大化。对于Redis的服务进程而言,在开始持久化时,它唯一需要做的只是fork出子进程,之后再由子进程完成这些持久化的工作,这样就可以极大的避免服务进程执行IO操作了。
4). 相比于AOF机制,如果数据集很大,RDB的启动效率会更高。
RDB又存在哪些劣势呢?
1). 如果你想保证数据的高可用性,即最大限度的避免数据丢失,那么RDB将不是一个很好的选择。因为系统一旦在定时持久化之前出现宕机现象,此前没有来得及写入磁盘的数据都将丢失。
2). 由于RDB是通过fork子进程来协助完成数据持久化工作的,因此,如果当数据集较大时,可能会导致整个服务器停止服务几百毫秒,甚至是1秒钟。
AOF的优势有哪些呢?
1). 该机制可以带来更高的数据安全性,即数据持久性。Redis中提供了3中同步策略,即每秒同步、每修改同步和不同步。事实上,每秒同步也是异步完成的,其效率也是非常高的,所差的是一旦系统出现宕机现象,那么这一秒钟之内修改的数据将会丢失。而每修改同步,我们可以将其视为同步持久化,即每次发生的数据变化都会被立即记录到磁盘中。可以预见,这种方式在效率上是最低的。至于无同步,无需多言,我想大家都能正确的理解它。
2). 由于该机制对日志文件的写入操作采用的是append模式,因此在写入过程中即使出现宕机现象,也不会破坏日志文件中已经存在的内容。然而如果我们本次操作只是写入了一半数据就出现了系统崩溃问题,不用担心,在Redis下一次启动之前,我们可以通过redis-check-aof工具来帮助我们解决数据一致性的问题。
3). 如果日志过大,Redis可以自动启用rewrite机制。即Redis以append模式不断的将修改数据写入到老的磁盘文件中,同时Redis还会创建一个新的文件用于记录此期间有哪些修改命令被执行。因此在进行rewrite切换时可以更好的保证数据安全性。
4). AOF包含一个格式清晰、易于理解的日志文件用于记录所有的修改操作。事实上,我们也可以通过该文件完成数据的重建。
AOF的劣势有哪些呢?
1). 对于相同数量的数据集而言,AOF文件通常要大于RDB文件。RDB 在恢复大数据集时的速度比 AOF 的恢复速度要快。
2). 根据同步策略的不同,AOF在运行效率上往往会慢于RDB。总之,每秒同步策略的效率是比较高的,同步禁用策略的效率和RDB一样高效。
二者选择的标准,就是看系统是愿意牺牲一些性能,换取更高的缓存一致性(aof),还是愿意写操作频繁的时候,不启用备份来换取更高的性能,待手动运行save的时候,再做备份(rdb)。rdb这个就更有些 eventually consistent的意思了。不过生产环境其实更多都是二者结合使用的。
转载地址:http://jmfh.baihongyu.com/
